The Right to Information (RTI) Act, 2005 gives every Indian citizen the power to seek information from government departments. This law promotes transparency and accountability, ensuring that authorities remain answerable for their actions. With RTI, people can request details about government policies, decisions, and public spending, making the system more open and efficient.
Filing an RTI is a simple process that can be done both online and offline. Whether you need information about public projects, government funds, or administrative decisions, the RTI Act allows you to obtain these details legally.
This blog provides a step-by-step guide on how to file an RTI application, the fees involved, and the expected response time. By using this tool effectively, citizens can promote good governance and fight corruption. Keep reading to learn how to file an RTI request hassle-free and make the most of your right to information.
Understanding the Right to Information (RTI) Act, 2005
Background:
Before the Right to Information (RTI) Act, 2005, government activities in India were largely opaque, and citizens had little access to official information. Corruption and misuse of power were common, as people had no legal way to question government decisions.
The push for transparency began in the early 1990s, led by activists like the Mazdoor Kisan Shakti Sangathan (MKSS) in Rajasthan. They fought for the right to access records of government spending on rural development projects. Their movement gained national attention, leading to the demand for a law ensuring citizen access to information.
In response, several states introduced RTI laws, and finally, in 2005, the RTI Act was passed at the national level. This law aimed to give people the power to hold the government accountable, reduce corruption, and promote good governance by making information more accessible to all.
What is the RTI Act?
The Right to Information (RTI) Act, 2005 is an important law that allows Indian citizens to request information from government departments. It was introduced to promote transparency and reduce corruption in public offices. Under this Act, any citizen can ask for records, documents, reports, or other data related to government decisions and policies. The government is legally required to provide the requested information within a fixed time unless it falls under specific exemptions, such as national security or personal privacy.
Objectives of the RTI Act
The RTI Act serves two key purposes:
- Empowering Citizens: It gives people the legal right to access government information, enabling them to stay informed about policies and decisions affecting their lives.
- Ensuring Accountability: By making government operations more transparent, RTI helps reduce corruption and ensures public officials are answerable for their actions.
This law strengthens democracy and promotes good governance by giving citizens a voice.
Eligibility to File an RTI Application
The Right to Information (RTI) Act, 2005, is a powerful law that allows Indian citizens to access information from government authorities. However, not everyone is eligible to file an RTI, and there are restrictions on the type of information that can be requested. Understanding who can file an RTI and what information can be accessed is essential to using this legal tool effectively.
Who Can File an RTI?
The RTI Act grants the right to information exclusively to Indian citizens. Here’s a clear breakdown of who is eligible to file an RTI:
- Any Indian citizen can file an RTI. Whether you are a student, working professional, or activist, you can request information from government departments.
- Organizations and companies cannot file RTIs directly. However, an individual associated with an organization can submit an RTI in their personal capacity.
- Foreign nationals are not allowed to file RTIs. The Act is meant exclusively for Indian citizens, restricting information access for non-citizens.
Understanding eligibility is important because only applications from Indian citizens will be considered valid by government authorities. Filing an RTI correctly ensures a higher chance of receiving the requested information without rejection.
Information Accessible Under RTI
The RTI Act enables individuals to obtain a wide range of information from government departments. This includes:
- Government policies, decisions, and programs. Citizens can ask about laws, schemes, and projects initiated by the government.
- Public expenditures and financial records. RTI can be used to track how taxpayer money is being spent.
- Official documents, memos, reports, and records. This includes meeting minutes, circulars, and other government communications.
- Contracts, tenders, and agreements. Citizens can request details of public contracts and procurement processes.
Exemptions Under the RTI Act
Not all information is accessible under RTI. The Act includes specific exemptions to prevent the misuse of sensitive data:
- National security-related information is restricted. Any data that could harm the integrity of the country, such as military operations or intelligence reports, is exempt from RTI requests.
- Personal information is protected. Citizens cannot access private data about other individuals unless it serves a larger public interest. This includes salary slips, medical records, and private communications.
- Trade secrets and intellectual property are restricted. Any information that could harm a company’s competitive position cannot be disclosed under RTI.
Why Understanding RTI Eligibility Matters
The Right to Information Act is a powerful tool for transparency and accountability in India. However, knowing the rules regarding eligibility and information access ensures that RTI applications are effective and not rejected. Citizens should always file clear, specific, and relevant RTI requests to receive accurate information without unnecessary delays.
By understanding these eligibility criteria and exemptions, individuals can use RTI efficiently to promote government transparency, fight corruption, and strengthen democracy.
Step-by-Step Guide to Filing an RTI Application
Filing a Right to Information (RTI) application in India is a straightforward process. You can submit an RTI request either offline (by writing a physical application) or online (through the government’s RTI portal). This guide explains both methods in detail.
Filing an RTI Application Offline
If you prefer traditional methods or need to file an RTI where online options are unavailable, you can submit a physical RTI application. Here’s how:
Step 1: the RTI Application
Your RTI application must be clear, precise, and properly formatted to ensure a response. The application should:
- Be written in English, Hindi, or the official language of the state where you are submitting the RTI.
- Be addressed to the Public Information Officer (PIO) of the concerned department. If unsure, you can check the official website of the relevant authority for PIO details.
- Include your full name, address, contact details, and a brief, specific query regarding the information you seek.
- Mention that you are seeking information under the RTI Act, 2005.
- If applicable, attach supporting documents that justify the request.
Sample RTI Application for Filing Offline
To,
The Public Information Officer (PIO),
[Name of the Department],
[Address of the Department],
[City, State, PIN Code]
Subject: Request for Information under the RTI Act, 2005
Respected Sir/Madam,
I, [Your Full Name], a resident of [Your Address], am filing this application under the Right to Information (RTI) Act, 2005, seeking the following information:
- [Clearly state the specific information you require.]
- [Mention any document copies you need, if applicable.]
As per Section 6(1) of the RTI Act, 2005, I request you to provide the required information within 30 days. If my request is transferred to another department, kindly inform me within 5 days as per the Act.
I have enclosed the RTI application fee of ₹10 via [Indian Postal Order (IPO)/Demand Draft/Banker’s Cheque/UPI]. I belong to the Below Poverty Line (BPL) category (if applicable) and have attached a copy of my BPL certificate for fee exemption.
Applicant Details:
- Full Name: [Your Name]
- Address: [Your Full Address]
- Phone Number: [Your Contact Number]
- Email (if available): [Your Email]
I kindly request you to provide the information at the earliest as per the provisions of the RTI Act.
Thank you.
Sincerely,
[Your Name]
[Your Signature]
[Date]
Step 2: Submission Methods
Once the application is prepared, you must submit it to the relevant government department. There are multiple ways to do this:
- By Post – Send the application via Speed Post or Registered Post to ensure tracking and proof of submission.
- In-Person Submission – Visit the public authority’s office and submit the application at the RTI Cell or PIO’s office. Request an acknowledgment receipt for reference.
If the RTI request is incorrectly sent to the wrong department, the authorities must transfer it to the correct department within five days under the RTI Act.
Step 3: Payment of Fees
To process your RTI request, a nominal fee of ₹10 is required. The payment can be made through:
- Indian Postal Order (IPO) – Available at post offices.
- Demand Draft (DD) or Banker’s Cheque – Issued in favor of the relevant department.
- Cash Payment – Some government offices accept direct cash payments (ask for a receipt).
Fee Exemptions
- Below Poverty Line (BPL) applicants are exempt from paying the fee. However, they must attach a copy of their BPL certificate as proof.
Filing an RTI Application Online
Filing an RTI online is quicker and more convenient. You can submit requests from anywhere using the official RTI portal: https://rtionline.gov.in/.
for offical detailed User manual : https://rtionline.gov.in/um_citizen.pdf
Step 1: Accessing the RTI Online Portal
Visit the official RTI Online website and read the guidelines carefully. This portal is managed by the Government of India and allows users to file RTI applications for Central Government departments and some state departments.
If you need to file an RTI for state government authorities, check if the respective state has a separate RTI portal.
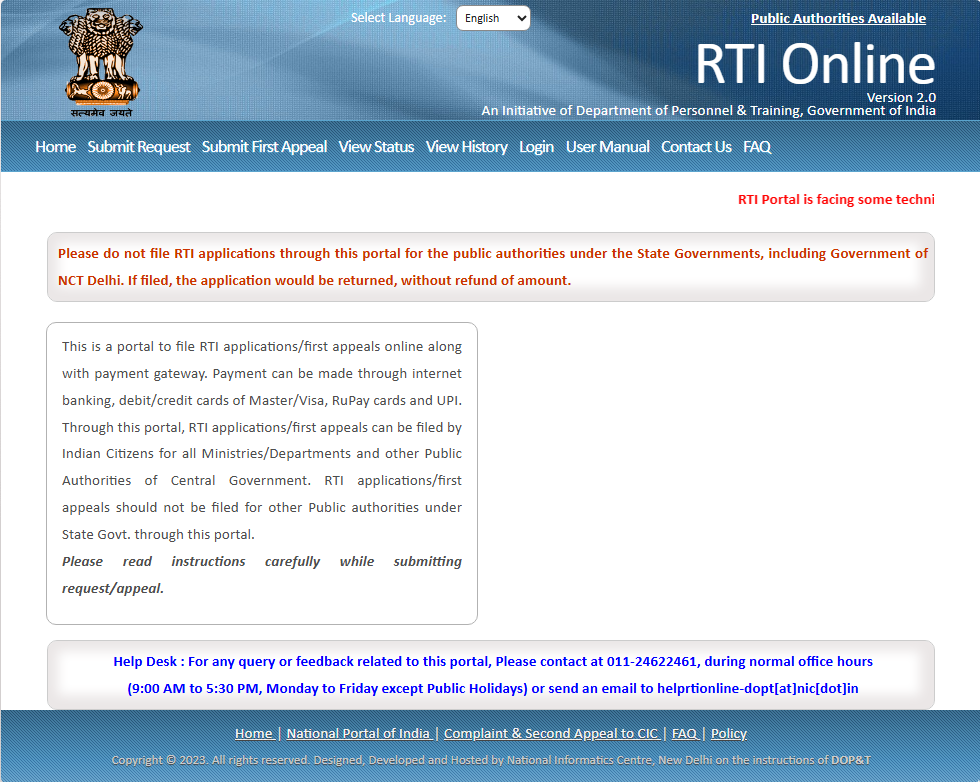
Step 2: Click on Submit Request
Before submitting an RTI request, you must have to checkbox on "I have read and understood the above guidelines.":
- after the clicking on checkbox you are ready to file your RTI online

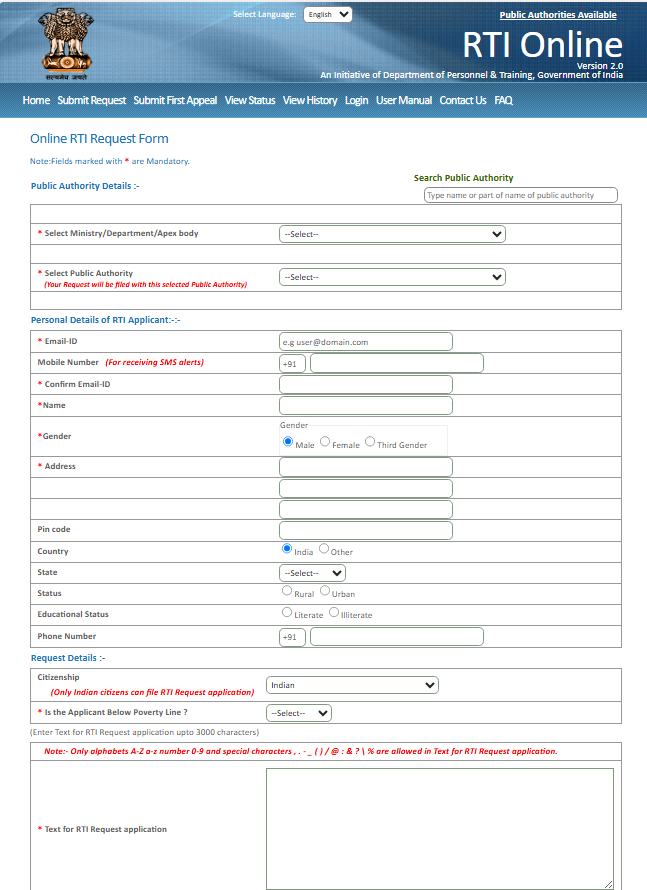
Step 3: Submitting the Application
After logging in, follow these steps to file your RTI request:
- Click on ‘Submit Request’ and select the public authority you wish to request information from.
- In the ‘Application Details’ section, clearly write your RTI request. Be specific and to the point to ensure a proper response.
- If needed, attach supporting documents (PDF format, max size 1 MB).
- Provide your personal details (name, address, and contact information).
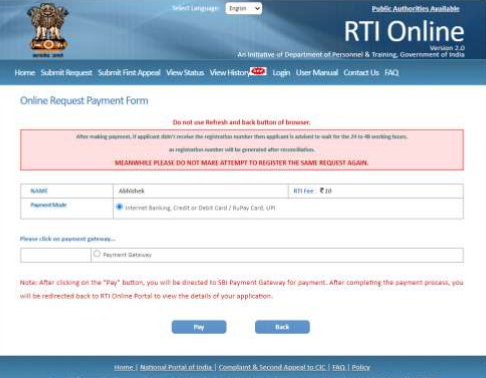
Step 4: Online Payment of Fees
To complete your RTI submission, pay the ₹10 application fee using available online payment options:
- Credit/Debit Card (Visa, Mastercard, RuPay)
- Net Banking
- UPI (Unified Payments Interface)
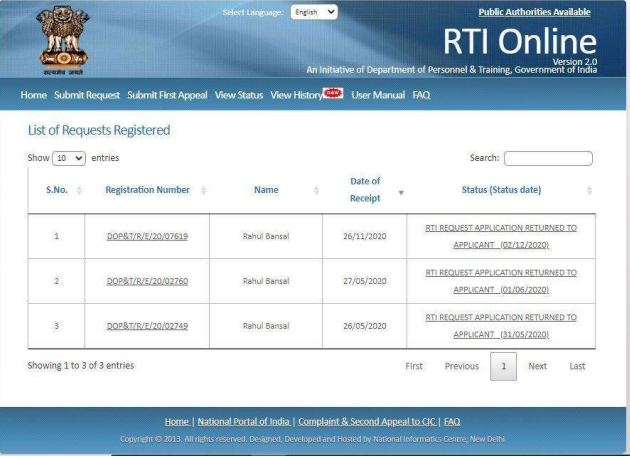
After successful payment, a unique RTI reference number is generated. Keep this number safe as it is required for:
- Tracking your application status.
- Filing an appeal if you do not receive a response within 30 days.
Fee Exemptions for Online RTI
If you belong to the Below Poverty Line (BPL) category, select the BPL option while filing the RTI and upload a scanned copy of your BPL certificate. The ₹10 fee is waived for BPL applicants.
Important Considerations When Filing an RTI
Filing an RTI is a powerful way to seek government information, but many applications get rejected due to common mistakes. Understanding what to avoid can improve the chances of receiving a clear and timely response.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Vague or unclear questions – RTI queries should be specific and precise to avoid rejection. For example, instead of asking "What are the education policies?", ask "Please provide copies of the policies related to primary education in Delhi for the year 2024."
- Requesting personal information – Information related to individuals (e.g., salaries, medical records) is exempted unless it is in the public interest.
- Submitting to the wrong department – If the RTI is sent to an incorrect authority, it may get delayed or rejected. Always research and ensure that the request is addressed to the right Public Information Officer (PIO).
- Not paying the correct fee – The RTI application fee is ₹10, but state rules may differ. Always confirm the applicable fee and payment method before submitting.
- Using disrespectful or accusatory language – RTI applications should be neutral and professional. Avoid making allegations or complaints, as they may lead to rejection.
Tips for a Successful RTI Application
- Be clear and to the point – Write short and direct questions to get an accurate response.
- Request copies of documents instead of opinions – Instead of asking “Why was this decision made?”, ask “Please provide a copy of the decision document.”
- Include contact details – Ensure your name, address, and phone number are mentioned correctly in the RTI application.
- Follow up if necessary – Track your RTI request using the application reference number and file an appeal if the response is unsatisfactory.
By following these tips, applicants can ensure that their RTI request is processed efficiently and that they receive the necessary information without unnecessary delays.
Most Asked Questions on Filing an RTI in India
- What is the Right to Information (RTI) Act, 2005?
Explain the purpose and significance of the RTI Act in promoting transparency and accountability in governance.
- Who can file an RTI application in India?
Clarify the eligibility criteria and whether organizations, foreign nationals, or companies can file RTI applications.
- How can I file an RTI application online?
Provide a step-by-step guide for filing RTI through the official portal https://rtionline.gov.in.
- How can I file an RTI application offline?
Explain the process of writing, submitting, and sending an RTI application via post or in-person.
- What type of information can be requested under RTI?
List the government-related data that citizens can access and mention any exemptions under the RTI Act.
- What is the RTI application fee, and how can I pay it?
Mention the ₹10 fee, accepted payment methods (online and offline), and fee exemptions for BPL applicants.
- How long does it take to receive an RTI response?
Explain the standard response time of 30 days, the 5-day transfer rule, and the 48-hour limit for urgent cases.
- What should I do if I don’t receive a response to my RTI application?
Guide users on filing a first and second appeal, including the respective authorities and deadlines.
- What are the common reasons for RTI rejection, and how can I avoid them?
Discuss unclear queries, personal data requests, wrong departments, and incorrect fees that lead to rejection.
- Can I track my RTI application status online?
Explain how applicants can use their RTI reference number to check the status of their request on the RTI portal.
